Friday 30 September 2022
What is Relational Operator in C++, JavaScript, Python, C Language |What is Relational Operator in Programming Language |What is Operator in programming Language |C++ Operators |How Many Operators are in C++ Language |What is Operators in Computer |What is Relational Operator in Computer
Wednesday 28 September 2022
What is Class and Object in C++ Hindi Explain |What is Class and Object in C language in hindi |What is Class & Object in Programming languages in hindi |What is Class in Programming language | What is Object in Programming language | Class and object in Programming Language C++, JavaScript explain in hindi
-: Class & Object in C++ :-
Class:-
C++ में, Class अपने स्वयं के गुणों(Attributes) और विधियों(Methods) के साथ एक बिल्डिंग ब्लॉक हैं। यहां गुण(Attribute) का अर्थ है अंदर उपलब्ध चर(variable) और विधियों(Methods) का अर्थ है कक्षा के अंदर उपलब्ध कार्य(Function).
Class, किसी विशिष्ट(specific) प्रकार के विषय से संबंधित डेटा या जानकारी के संग्रह के लिए एक बुनियादी संरचना(Basic Structure) या एक Blueprint कहा जा सकता है।
उदाहरण के लिए: - हमारे पास एक कार शोरूम है, जहां विभिन्न कारें उपलब्ध हैं। क्योंकि कारें अलग हैं मतलब उनके गुण(Attribute) भी अलग होंगे, जैसे मूल्य(Price) , ब्रांड नाम(Brand Name) , ईंधन प्रकार(Fuel Type). तो यहां प्रत्येक कार से संबंधित personal डेटा के साथ सभी कारों की जानकारी संग्रहीत करने के लिए एक Class बनाया जाएगा।
class CarInfo{
public:
DataType Price ;
DataType Brand;
DataType FuelType ;
};
Objects :-
Object वास्तविक विश्व इकाई(real world entity) है जिसमें कोई भी अवस्था(state) और व्यवहार(behavior) होता है। यदि इसका कोई State है तो निश्चित रूप से इसके state से संबंधित डेटा होगा और यदि इसका कोई behavior है तो निश्चित रूप से इसके behavior से संबंधित डेटा होगा अर्थात निश्चित रूप से इसकी कोई कार्यक्षमता(functionality) होगी।
Object के नाम के बाद डॉट (.) ऑपरेटर का उपयोग करके हम class की property और विधियों(Methods) तक पहुंच(can access) सकते हैं।
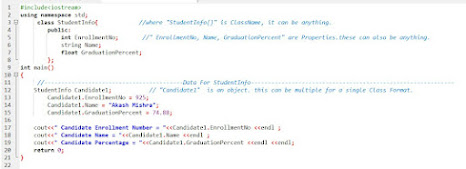
basics structure of Class with Object -
________________________________________________________________________
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class CarInfo{
public:
int Price ;
string BrandName ;
string FuelType;
FunctionName() {
Statements
}
}
int main() {
CarInfo car1, car2;
car1.Price = 1500000;
car2.Price = 8000000;
car1.FuelType = "Diesel" ;
car2.FuelType = "Petrol" ;
cout<< "price of car1 = " << car1.Price <<endl;
cout<< "car1 Fuel Type =" <<car1.FuelType <<endl;
cout<< "price of car2 = " << car2.Price <<endl;
cout<< "car2 Fuel Type = " <<car2.FuelType <<endl;
return 0;
}
________________________________________________________________________
output:-
price of car1 = 1500000
car1 Fuel Type = Diesel
price of car2 = 8000000
car2 Fuel Type = Petrol
According to definition, Class के अंदर के function को विधि(method) कहा जाता है और class के अंदर के चर(variable) को गुण(property) या विशेषता(Attribute) कहा जाता है। मूल्य, ब्रांडनाम और फ्यूल टाइप निर्मित class के गुण हैं जहां FunctionName() एक ही class के अंदर एक function है।
________________________________________________________________________
Click on image to see clear view
What is Class and Object in C++ |What is Class and Object in C language |What is Class & Object in Programming languages |What is Class in Programming language | What is Object in Programming language | Class and object in Programming Language C++, JavaScript,
-: Class & Object in C++ :-
Class:-
In the C++, the classes are a building blocks along with their own properties and methods. Here Properties means Variables available inside and methods means Function available inside the class.
A class is a basic structure or can say a blueprint for a collection of data or information related to any specific kind of Subject.
For Example:- we have a car showroom with different cars & their properties like price, brand name, fuel type . So here A class will be created to store All Cars information with data related to the each car.
class CarInfo{
public:
DataType Price ;
DataType Brand;
DataType FuelType ;
};
Objects :-
An object is an instance of Class. Object is a real world entity that has any state and behavior. If it has any state means Definitely it would have data related to its state and behavior means Definitely it would have any functionality.
By using dott(.) operator after objectName we can access the property and methods of Class.
basics structure of Class with Object -
________________________________________________________________________
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class CarInfo{
public:
int Price ;
string BrandName ;
string FuelType;
FunctionName() {
Statements
}
}
int main() {
CarInfo car1, car2;
car1.Price = 1500000;
car2.Price = 8000000;
car1.FuelType = "Diesel" ;
car2.FuelType = "Petrol" ;
cout<< "price of car1 = " << car1.Price <<endl;
cout<< "car1 Fuel Type = " <<car1.FuelType <<endl;
cout<< "price of car2 = " << car2.Price <<endl;
cout<< "car2 Fuel Type = " <<car2.FuelType <<endl;
________________________________________________________________________
output:-
price of car1 = 1500000
car1 Fuel Type = Diesel
price of car2 = 8000000
car2 Fuel Type = Petrol
According to the definition , The Function inside the class is called as Method and Variable inside the Class is called Property or Attribute. Price, BrandName and FuelType are properties of created Class where FunctionName() is a function inside the same Class.
________________________________________________________________________
Click on image to see clear view
Tuesday 27 September 2022
What is Function in programming language in hindi |Programming language Function in hindi | Programming Language me function kya Hai |Computer me function kya Hai |C++ Language me function kya hai |Functions in C++ Language
-:प्रोग्रामिंग Language में Function क्या है? :-
Function
Function कोड का एक ब्लॉक है, जो एक बार बनाया जाता है और जरूरत पड़ने पर इसे हमारे प्रोग्राम में बार-बार इस्तेमाल किया जाता है।
Function तब run करता है जब इसे प्रोग्राम के अंदर बुलाया जाता है। विभिन्न उद्देश्यों (Operations) की पूर्ति के लिए विभिन्न Function बनाते हैं।
___________________________________________________________
- Basic Syntax of Function in C++ is written below -
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
DataType FunctionName( Parameter1, parameter 2,.......){
Return WriteOperationToBePerform(example +, -, *, / etc);
}
int main() {
cout<<FunctionName(value1, value2,......) ;
return 0 ;
}
___________________________________________________________
- : आइए एक उदाहरण देखें कि फ़ंक्शन कैसे बनाएं और उपयोग करें :-
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int AddFunc(int X, int Y) {
return X + Y; }
int SubFunc(int A, int B) {
return A - B; }
int MulFunc(int P, int Q) {
return P * Q; }
int DivFunc(int M, int N) {
return M/N ;}
int main() {
cout<<"Summation of X & Y = " <<AddFunc(10, 5) <<endl;
cout<<"Subtraction of A & B= " <<SubFunc(50, 20) <<endl;
cout<<"Product of P & Q = " <<MulFunc(15, 2) <<endl;
cout<<"Division of M & N = " <<DivFunc(40,20) ;
return 0 ;
}
___________________________________________________________
output :- Summation of X & Y = 15
Subtraction of A & B= 30
Product of P & Q = 30
Division of X & Y = 2
___________________________________________________________
Click on image to see clear view
Output:-
यदि हम किसी special purpose or operation के लिए एक लंबा program लिखते हैं और हमें दो संख्याओं को कई बार जोड़ना होता है, तो एक ही कोड को बार-बार लिखने के बजाय, हम केवल उस function को कॉल करेंगे जो विशेष रूप से दो संख्याओं को जोड़ने के लिए लिखा गया है और parameter-1 और parameter-2 के स्थान केवल दो नए मान assign करें जो जोड़ा जाना है।
- single purpose की पूर्ति के लिए कोड की पुनरावृत्ति से बचने के लिए।
- हमारे program को साफ रखने के लिए।
- हमारे program को छोटा करने के लिए |
What is Operators in C++| Types of Operators in C++ |Types of Operators in C Language |Arithmetic Operator in C++ |What is Operators in Programming Language|Operators in Computer |
-: Operators in Programming Languages :-
Operators -
In the programing Languages, operators are those symbols which are used between operands to perform any operation.
For Example :- 4 + 7 = 12
where,
(4) and (7) are Operands
(+) and (=) sign are Operators
Types of Operators in C++ Language :-
- Arithmetic Operators (+, -, *, /, %)
- Relational Operators (<, >, ==, !=, <=, >=)
- Logical Operators (&&, ||, !)
- Bitwise Operators (&, |, ~, ^, >>, <<)
- Increment Decrement Operators (++, - -)
- Assignment Operators (=, +=, - =, *=, /=)
- Conditional or Ternary Operators (?, :)
- Special or Other Operator (sizeof() )
OUTPUT :-
Addition Of Two Numbers = 15
Difference of Two Numbers = 5
Product of Two Numbers = 50
Division of Two Numbers = 2
Module of Two Numbers = 0
where , Module
(%) gives us remainder as a results.
Monday 26 September 2022
What is Function in programming language |what is function in C++ |what is function call in programming language |what is function in computer |What is function in programming
-: Functions in C++ :-
Function is a block of code, which created once and reused it again and again in our programme anywhere when needed.
Function runs when it is called inside the program. To serve different purposes(operations) create different functions.
- Basic Syntax of Function in C++ is written below -
__________________________________________________________
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
DataType FunctionName( Parameter1, parameter 2,.......){
Return WriteOperationToBePerformed(example +, -, *, / etc);
}
int main() {
cout<<FunctionName(value1, value2,......) ;
return 0 ;
}
___________________________________________________________
-:Let's See one example for how to create and use functions:-
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int AddFunc(int X, int Y) {
return X + Y; }
int SubFunc(int A, int B) {
return A - B; }
int MulFunc(int P, int Q) {
return P * Q; }
int DivFunc(int M, int N) {
return M/N ;}
int main() {
cout<<"Summation of X & Y = " <<AddFunc(10, 5) <<endl;
cout<<"Subtraction of A & B= " <<SubFunc(50, 20) <<endl;
cout<<"Product of P & Q = " <<MulFunc(15, 2) <<endl;
cout<<"Division of M & N = " <<DivFunc(40,20) <<endl;
return 0 ;
}
___________________________________________________________
output :- Summation of X & Y = 15
Subtraction of A & B= 30
Product of P & Q = 30
Division of X & Y = 2
___________________________________________________________
Click on image to see clear view
let's understand that what happened above -
- firstly we created a function with FunctionName SumFunc() and passed two parameters as container to contain those values which are to be added at the time of function run.
- where we took X and Y as parameter-1 and parameter-2 respectively.
- similarly we created 3 another functions for subtraction, multiplication and division.
- After successfully creating all functions we simply called these functions by their FunctionName [SumFunc(), SubFunc(), MulFunc(), DivFunc()]. it is not necessary to call these functions in same sequence, at a same time we can call either single or multiple functions too as we needed.
- On Calling Function, in the place of parameter-1 and parameter-2 we assigned directly values 10 and 5 respectively. You can put any value there.
- To avoid repetition of code to serve single purpose.
- To keep clean our programme.
- To make shorter our programme.
Must Read :-
What is function in programming language (Hindi explanation)
what is class in programming language C++
Sunday 25 September 2022
zeroth Law of Thermodynamics |First Law of Thermodynamics |Law of conservation of Energy |
-: Thermodynamics Laws :-
Zeroth Law :-
zeroth law of thermodynamics states that if two thermodynamic systems are in thermal equilibrium with third system, so we can say that they all are in thermal with each other .
in simple words- if system X is in thermal equilibrium with system Y, and system Y is in thermal equilibrium with system Z. Then X, Y, Z will be in thermal equilibrium with each other.
lets understand this with an example given below -
if we try to understand this in mathematical manner, so we can explain it like this -
let system X = system Y ...........(1)
system Y = system Z ..........(2)
from eq.(1) & (2), we get
system X = system Z _proved
So in the mathematical manner, we can prove the zeroth law of thermodynamics statement.
First Law or Law of conservation of Energy:-
First Law of Thermodynamics states that Energy of the Universe remains same. It neither can be created nor be destroyed, only can be convert into one form to another form.
in other words- Any thermodynamics system in equilibrium state posses a state called internal energy(E). Between any 2 equilibrium states, the change in internal energy is equal to the difference of the heat transfer into the system and work done by the system.
lets understand this in detail with a most suitable example-
here in the figure shown above, system-A is having higher energy than system-B, and heat transfer takes place between both systems. As we know that heat transfer takes place from higher temperature to lower temperature.
now Q heat started to travel from higher temperature system-A having energyE1 towards lower temperature system-B having energyE2. But heat Q travelled a path before reaching the system-B that means some work W is done by Q heat done to reach its final destination(system-B). So some Q heat is lost in the form of work W during the travel from A to B. So we can write it as -
E2 - E1 = Q - W
or ΔE = Q - W
as system-B is taking energy hence E2 is positive.
system-A is giving energy hence E1 is negative.
similarly if work done on system ,so W will be negative.
if work done by system, so W will be positive.
where,
E1 = available initial energy of system-A
E2 = available initial energy of system-B
ΔE = change in internal energy(E1-E2),
W = work done by system during travelling the path, to reach the B = (Q - Q1)
Q = Total heat, started to travel to reach the system-B
Q1 = energy lost, in the path travelling from A to B.
Saturday 24 September 2022
Difference Between Frame and Chassis | what is frame and chassis in automobile | Types of Frame in automobile | types of chassis in automobile
-: Difference Between Frame & Chassis :-
Frame:-
- it is the supporting base structure of the vehicle without mountings.
- The chassis is attached to the frame.
- Frame are made of box, tubular channel or U-shaped section welded or riveted together.
- In simple words - frames are that structure of a vehicle on which a the mountings (transmission, wheels, steering systems) remains mounted.
- It bears all the vehicles components as well as passengers load.
- Ladder frame
- Backbone frame
- X-frame
- Unibody
- A structure of vehicle including Metallic Frame with other mountings (transmission, wheels, steering systems etc).
- As most of the mounting works are done on the frame, so it is also called as framework of vehicle.
- it can be easily understand as Chassis = frame + mountings.
- Conventional or Framed Chassis.
- Non-conventional or Frameless Chassis.
Friday 23 September 2022
What is Stress | Difference Between Stress and Strain | What is Strain ? Stress & Strain formula |What is Stress in Engineering Mechanics | Unit of Stress
-: Difference between STRESS and STRAIN :-
Stress :-
- Stress is the intensity of internal resisting forces (to oppose the applied pressure) developed at a point.
- in other words - it is a internal resistive force to deformation per unit area.
- Stress may act either normal or parallel to the surface.
- Magnitude of the stress at a point is unequal in all the directions.
- Stress can be Tensile, Compressive or Shear type.
- Due to stress Pressure will not be developed.
Stress = F/A in N/meterSq.where F = internal resistive force developed (external) in NA = Area in meterSq.
Strain:-
- The ratio of change in length to actual length is called Strain.
- When a force get applied on the body, length of that body either increases or decreases.
- If length of body increases means the applied force is Tensile(+F) where if length decreases means the applied force is Compressive(-F) in nature.
- In other words, The ratio of Change in dimension to the Original Dimension is called Strain.
Strain(ε) = ΔL/L = (L1 - L)/L
Where ΔL = change in length
L = actual length.
L1 = New Length after force applied.
[Note:- in case of compressive force, Direction of forces shown in the figure will be inward.]
Difference between Pressure & Stress ?
Difference between Frame & Chassis ?
-
Thursday 22 September 2022
Difference Between Pressure and Stress | What is Stress | What is Pressure |Stress in Engineering
-: Pressure and Stress :
Pressure :-
- Pressure represents the intensity of external or outside forces exerting or acting at a point.
- in other words - it is the amount of external force applied per unit area.
- Magnitude of the Pressure at a point, remains same in all the direction.
- Due to pressure Stress will be developed.
Stress :-
- Stress is the intensity of internal resisting forces (to oppose the applied pressure) developed at a point.
- in other words - it is a internal resistive force to deformation per unit area.
- Stress may act either normal or parallel to the surface.
- Magnitude of the stress at a point is unequal in all the directions.
- Stress can be Tensile, Compressive or Shear type.
- Due to stress Pressure will not be developed.
-
- : Overloading in C++ :- When two or more members having same name but different parameters or datatypes are called Overloading ...
-
-: DTSI Technology :- In this Blog we will learn about introduction of DTSI Technology in Engines with its advantages and Examples. DTSI st...
-
-: Class & Object in C++ :- Class:- In the C++, the classes are a building blocks along with their own properties and...




.jpg)

.jpg)











